An Economics of Being Anonymous: Understanding Dark Web Marketplace Dynamics
Lately, the illicit web has earned a reputation as a haven for illegal actions and unregulated commerce. The attraction of anonymity offered by illicit platforms has captivated countless individuals seeking everything from both lawful and unlawful products to targeted services. Understanding the economics at play in these concealed marketplaces requires a thorough analysis of their unique dynamics, the range of stakeholders and the elements leading to their evolution.
Hidden markets operate beyond mainstream economic systems, often enveloped in a cover of anonymity. This environment fosters both innovation and risk, empowering participants to maneuver through a complex landscape of buyer-seller interactions while also facing the looming threats of law enforcement and digital offenses. Exploring darknet site between privacy, faith, and availability and desire within these markets reveals not only their appeal but also the difficulties that arise from them.
Market Structure of the Dark Web
The deep web is characterized by a unique market structure that operates outside the purview of traditional economic systems. It consists of a range of venues, known as black markets, where users can anonymously buy and sell a wide array of products and services. These markets function on concepts of supply and demand, with offerings ranging from drugs to cyber services, and even digital currencies. The anonymity afforded by encryption and privacy protocols is a key feature that attracts both buyers and sellers, creating a unique ecosystem driven by secrecy and often illicit activities.
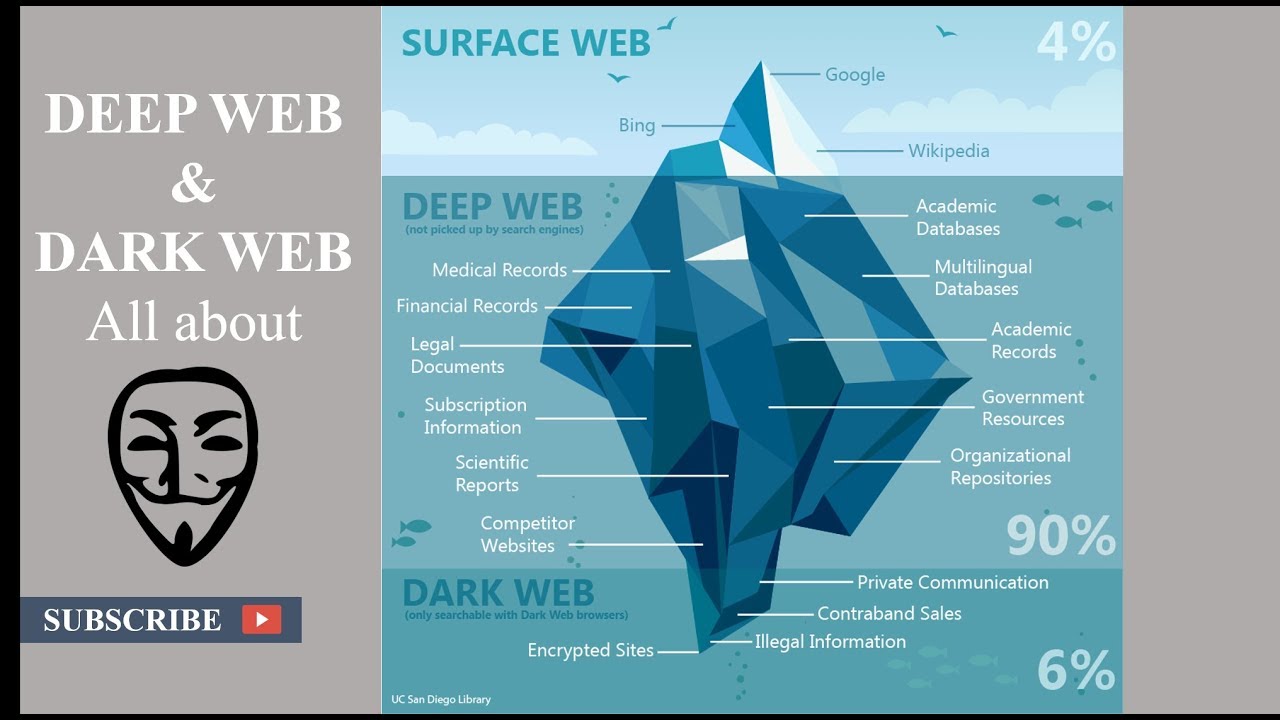
Within this structure, the organization of dark web markets is often distributed. Unlike conventional markets that may be dominated by a few large players, darknet markets usually comprise many small vendors competing for customers. This competition can lead to fluctuating prices and varying quality of goods. Additionally, the use of escrow services within transactions helps to build trust among users, mitigating the risks associated with online fraud. The decentralized nature also means that when one market is shut down, others can quickly emerge, maintaining an ongoing cycle of market evolution.
The economic dynamics of the dark web are further influenced by the community and feedback mechanisms in place. User feedback, ratings, and transaction histories play a pivotal role in vendor trustworthiness and consumer behavior. Buyers often depend on reviews and past experiences to make informed decisions, while sellers attempt to cultivate a positive reputation to attract more clients. This interconnected web of trust creates a more stable market environment, despite the inherent risks and legal consequences associated with operating in the anonymity of the dark web.
Main Participants and Stakeholders
Within the dark web ecosystem, there are several critical actors who drive the market dynamics. These include vendors, who are usually responsible for supplying items and offerings, and buyers, who seek to purchase these products. Vendors operate with different levels of business acumen, ranging from well-structured sellers to individuals engaging in sporadic sales. The extent to which they employ encryption and privacy tools often determines their success and longevity in the market. Their credibility is vital, as feedback from prior transactions establishes trust and credibility in a largely unidentified environment.
Another important stakeholder is the transaction processor. In darknet markets, cryptocurrencies, particularly Bitcoin, serve as the primary means of exchanges due to their private nature, allowing for a degree of disguise. However, specialized services such as anonymity services and coin shufflers also appear to further obfuscate the transaction trails, appealing to both vendors and buyers. These processors not only enable transactions but also sometimes engage in money laundering, which adds a dimension of complexity to the financial interactions of the dark web.
Lastly, authorities and regulatory agencies play a significant role as stakeholders, regularly adapting to the developing landscape of dark web markets. Their existence creates a friction between market participants, as authorities work to dismantle illegal operations while criminals innovate ways to evade detection. This ongoing battle influences the economic dynamics, impacting vendors’ operational plans and buyers’ actions as they navigate risks associated with anonymity and police oversight.
Financial Drivers Influencing Darknet Activity
The underground internet runs on a set of financial forces that differ significantly from conventional economies. One of the most important factors is the privacy given to individuals. This privacy attracts individuals looking to obtain or sell items and facilities that may be unlawful or scrutinized in the traditional market. The absence of regulatory allows for cost fluctuations that can change widely depending on demand and supply, frequently resulting in enhanced costs for particular goods while rendering others more accessible.
Furthermore, the availability of various digital currencies as the main way of exchange powers the underground internet marketplace. These cryptographic currencies offer users a level of anonymity and security that conventional transaction systems are unable. The volatility of virtual currencies can lead to speculative trading practices among traders, often creating a uncertain marketplace where traders seek to benefit on price variations. This situation further reinforces the pattern of acquiring and trading, as individuals endeavor to take advantage of the environment for financial benefit.
Finally, the cutthroat character of underground internet economies drives continual innovation among vendors. Merchants often work to distinguish their products through item excellence, user service, and distinct attributes. This competition fosters an atmosphere where more advanced products and services are frequently released, including increasingly structured marketplace models resembling standard business models. As a result, the underground internet is not just a sanctuary for prohibited behavior but also a intricate financial system shaped by its distinctive forces.